Download:
Brochure of SORPAS®
Demo CD of SORPAS® 2D |
"We have been using SORPAS® since 2001 and have made many innovative developments in resistance welding. We are now further extending the applications of simulation to process optimization for supporting production planning."
- Mr. Matthias Graul
Volkswagen AG, Germany |
 |
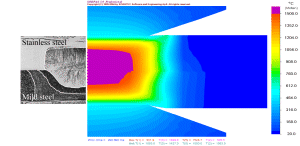
SORPAS® is dedicated professional software for simulation and optimization of resistance welding processes. It has been specially developed for engineers by engineers. It doesn't need any prior knowledge in numerical simulations, but can be easily learned and used by engineers with knowledge of welding and materials. The integration of welding expertise with numerical techniques has made SORPAS® a unique and powerful tool for engineers directly working in industry.
The build-in material database in SORPAS® has included nearly all commonly used metal materials including all types of steels, aluminum alloys, titanium alloys, copper alloys, nickel based alloys, surface coating materials, pure metals and high melting metals such as tungsten and molybdenum etc. The users can also add their own materials. It is possible to simulate with dimensions of weld parts ranging from ordinary sizes in millimeters down to micro sizes in a fraction of micron with welding machines of all types of power sources including AC, DC, MFDC, inverter, and capacitor discharge.
Benefits:
 Save costs Save costs
- Reduce lead time / time to market
- Speed up production running-in
- Improve weld quality
- Increase production stability
- Facilitate innovation
- Modernize technology
> Numerous new inventions have been
supported with SORPASŪ simulations >
Applications:
SORPAS® has been applied in various industries for solving problems
in spot welding, projection welding, butt welding and micro resistance
welding and supporting research and development as well as process
parameter optimizations.
|
|
- Evaluating weldability of materials
- Evaluating design of weld combinations
- Evaluating design of electrodes
- Inventing new applications
More details of applications are described in
industries.
|
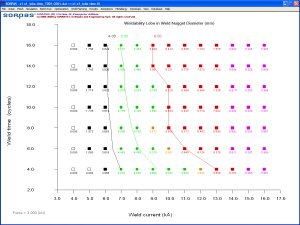
- Predicting weldability lobes and weld growth curves
- Optimizing process parameter settings
- Determining welding and cooling procedures
- Trouble shooting welding problems
|
Types of Licenses:
SORPAS® can be obtained in two types of license: special license
or leased license. For special license, the user will pay an upfront
license price for the first year and then a lower license fee from
the second year. For leased license, the user will only pay for
the specified period. One license means one installation of the
software on one computer.
Software Editions:
In order to satisfy various requirements of individual users, three
editions of SORPAS® are available as listed in the table below.
The Enterprise Edition is with the automated procedures for process
parameter optimizations including prediction of the weld growth
curves and weldability lobes as well as verification of contact
resistance, giving users the ultimate benefits to ensure before
welding.
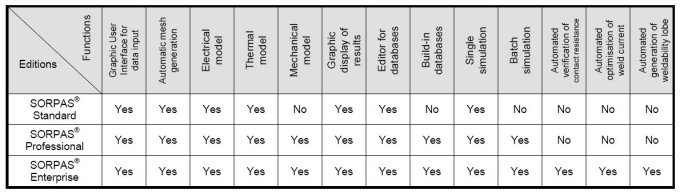
Explanation of the main functions:
- Graphic user interface for data input: include
the New Input Wizard and the Data file editor for design of geometries
and selection of materials (from integrated databases) for electrodes,
weld parts and coatings, and settings of welding process parameters.
- Automatic mesh generation: automatically generate
FEM mesh for spot welding and/or according to user defined number
of elements and density distributions.
- Electrical model: calculates the current distribution
and heat generation depending on types of weld current and materials
of weld combinations.
- Thermal model (including optional metallurgical model):
calculates the heat transfer, temperature development, materials
properties changing with temperature, and weld nugget formation.
- Mechanical model: calculates the mechanical
reactions including deformation of materials, evolution of contact
areas at interfaces, stress and strain status depending on welding
machine characteristics and dynamics.
- Graphic display of results: display of simulation
results including curves of process parameters and animations
of the evolution of variable (temperature, current etc.) distribution
and development of the weld nugget shape and size in each material.
- Editor for databases: the user interface for
editing (adding, removing and modifying) data in the three integrated
databases for material properties, electrode forms and designs
of workpieces.
- Build-in databases: three database are integrated
in the software system including the material database with properties
of most commonly used standard materials, the electrode database
with most standard electrode forms (ISO 5821), and the workpiece
database for retrievable design of weld parts.
- Single simulation: simulation of one specific
welding process with specified electrode and material combinations,
and given process parameter settings (weld current, force and
time etc.).
- Batch simulation: run a batch of simulations
following a list of predefined data files of different welding
conditions or procedures for process optimization.
Automated verification of contact resistance: automatically verify
the contact resistance factors against a tested weld nugget for
verifying data of new materials.
- Automated verification of contact resistance: automatically verify the contact resistance factors against a tested weld nugget size for verifying
the data of new materials.
- Automated optimization of weld current: two
optimization functions are implemented for optimization of the
weld current. One is for automatically running a series of simulations
according to user-defined range of weld current from a lower limit
to a higher limit with a given increment, whereby the weld growth
curve will be generated. The other one is for automatically running
simulations to seek for the optimal weld current according to
a targeted objective diameter of the weld nugget.
- Automated generation of weldability lobe: two
types of the weldability lobes can be generated automatically
following the procedures recommended in ISO 14327:2004, where
two process parameters are varied. One type is to vary the weld
current and time while keep weld force constant. The other type
is to vary the weld current and force while keep the weld time
constant. The splash limits are predicted and the weld ranges
are indicated according to three reference weld nugget diameters
(minimum, maximum and nominal) which are given by users.
|

 Save costs
Save costs